While you are pregnant, you can check the health and development of the baby that you are carrying. These health checks are the NIPT, the 13-week scan and the 20-week scan. This is called prenatal screening.
What tests are available?
Noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is a blood test to check for chromosomal abnormalities. The 13-week scan and the 20-week scan use an ultrasound to check for physical abnormalities. It is up to you to decide whether to have these tests.
Which tests can you have and when?
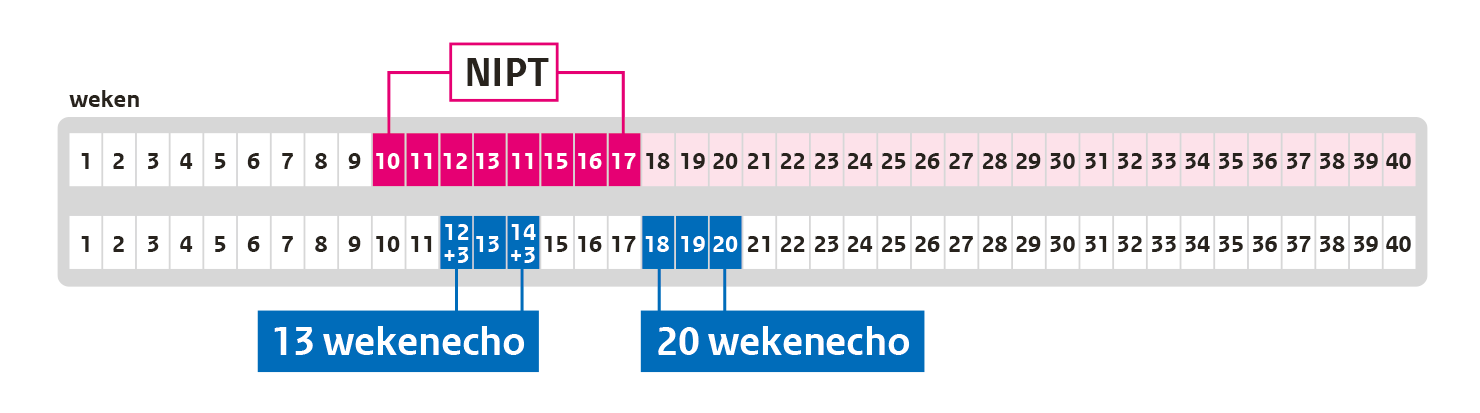
- From week 10:
NIPT: test for chromosomal abnormalities - About week 13:
13-week scan: test for physical abnormalities early in the pregnancy - About week 20:
20-week scan: test for physical abnormalities , about (almost) halfway through the pregnancy
Making a choice
When you see your midwife for the first time, you will be asked if you would like to know more about the options for prenatal screening. This includes more details about the NIPT and the 13-week and 20-week scan.
There are two options:
- You would prefer not to know. You will not receive any information and you will not have the tests.
- You would prefer to know. You will have an in-depth consultation. The midwife will help you consider what you need in order to make a choice that is appropriate for you. You can also ask questions. After the in-depth consultation, you will decide whether or not you want to have one or more tests.
- Here are some questions to consider carefully:
- How much do you want to know about your child when you are pregnant’
- What would it be like for you to live with a child who has a chromosomal abnormality such as Down syndrome, or a child who has a physical abnormality?
The NIPT
What is the NIPT?
Noninvasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is a blood test to check for chromosomal abnormalities in an unborn baby. If you opt to have the NIPT, your blood will be tested for chromosomal abnormalities that could have serious consequences for the child’s health, such as Down syndrome.
The NIPT involves giving a blood sample. You can have blood drawn from week 10 of your pregnancy. Your midwife or gynaecologist will tell you where to go to have your blood drawn. After that, your blood with be tested. The NIPT is free of charge.
We have chromosomes in every cell in our body. These chromosomes are made up of DNA. Your DNA determines your physical characteristics: for example, height, eye colour, and how everything in your body works. Each cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes. Sometimes there is a problem when the chromosomes are formed. This is called a chromosomal abnormality, also known as a genetic disorder.
There are various types of chromosomal abnormalities:
An extra chromosome: one too many
- Down syndrome. People with Down syndrome have intellectual disabilities, as well as characteristic physical features of the syndrome. Children with Down syndrome have developmental delays and are more likely to have physical and intellectual disabilities. The average life expectancy for people with Down syndrome is 60 years old. They will need guidance and support from their families or others throughout their lives.
- Edwards’ syndrome and Patau’s syndrome. These genetic disorders are very severe. Most children with Edwards’ syndrome or Patau’s syndrome do not survive to the end of the pregnancy, or die soon after birth.
Missing or extra portion of a chromosome
- These chromosomal abnormalities are usually very serious. The child may have intellectual disabilities and one or more physical defects as a result.
The results of the NIPT do not provide a 100% guarantee. Still, the results are usually reassuring: if the NIPT shows no indications of a chromosomal abnormality, your child is very unlikely to have one.
What if the results do show evidence of a chromosomal abnormality? Then you can have follow-up diagnostic testing to confirm whether the abnormality is actually present in the child. Even if a chromosomal abnormality is found, it could come from the placenta, or (very rarely) from the mother. Your midwife can tell you more. It is up to you to decide whether you want to have follow-up tests. A chromosomal abnormality in a child always has serious consequences. But you cannot predict how serious it will be. It is difficult for every child.
The NIPT results are available within 10 days.
There is no evidence of any chromosomal abnormality
About 993 in 1000 pregnant people get this result. It is almost always accurate. Fewer than 1 in 1000 pregnant people are carrying a child with a chromosomal abnormality. No follow-up diagnostic testing is needed.
There is evidence of a chromosomal abnormality
About 7 in 1000 pregnant people get this result. You may be carrying a child with a chromosomal abnormality. There are two options:
- There is evidence of Down syndrome, Edwards’ syndrome or Patau’s syndrome. You will receive a phone call from a medical professional who can counsel you. This will usually be your midwife.
- There is evidence of some other chromosomal abnormality. You will be called by a doctor (clinical geneticist) from a university hospital.
The doctor will invite you for an appointment to discuss the results. You will receive more information about the specific chromosomal abnormality and what options are available for follow-up diagnostic testing.
The test did not work
About 20 in 1000 pregnant people get this result. If the first test did not work, you can choose to repeat the NIPT. The second NIPT test is usually successful, for approximately 4 in 5 pregnant women is this the case.
The 13-week scan and the 20-week scan
In the 13-week scan and the 20-week scan, a sonographer uses an ultrasound machine to check if the unborn child has any physical abnormalities. The sonographer also checks how much amniotic fluid is present and how the unborn child is growing.
The 20-week scan is very similar to the 13-week scan, but there are differences.
The 13-week scan and 20-week scan can only be done by specially trained sonographers. The sonographer makes a scan of your unborn child by moving the transducer of the ultrasound machine over your abdomen. The scan does not hurt at all and is not dangerous. Your unborn child will not feel anything. The scan will take about 30 minutes. You do not have to pay anything for the 13-week scan or the 20-week scan.
You can have the 13-week scan done in week 12+3 until week 14+3 of your pregnancy. That means the scan can be done from 12 weeks and 3 days until 14 weeks and 3 days of pregnancy. Note: In the Netherlands, you will only be able to have the 13-week scan if you participate in the scientific IMITAS study (webpage in Dutch). The IMITAS study is investigating the advantages and disadvantages of the 13-week scan.
You can have the 20-week scan done in week 18+0 until week 21+0 of your pregnancy. That means the scan can be done from 18 weeks and 0 days until 21 weeks and 0 days of pregnancy. The ideal time for this scan is in week 19 of your pregnancy: from 19 weeks and 0 days until 19 weeks and 6 days of pregnancy.
The sonographer cannot see all physical abnormalities on the 13-week scan or the 20-week scan. That means that your unborn child may have a birth defect, even if the ultrasound scan does not show any physical abnormalities.
The sonographer will tell you the results right after the ultrasound scan.
- There is no evidence of physical abnormalities. About 990 in 1000 pregnant people get this result.
- The sonographer did a visual check of the unborn child, but could not see everything clearly.
- An abnormality was observed. About 10 in 1000 pregnant people get this result. You can choose to have follow-up diagnostic testing.
- There is no evidence of abnormalities. About 950 in 1000 pregnant people get this result.
- The sonographer wants to repeat the scan.
- An abnormality was observed. Follow-up diagnostic testing is needed to confirm. About 50 in 1000 pregnant people get this result.
- An abnormality was observed, but its significance is not yet known. Follow-up diagnostic testing is not needed. You will have another ultrasound scan later in your pregnancy. During that scan, the sonographer checks if the abnormality is still present or if the abnormality has resolved.
Follow-up diagnostic testing
When can you have follow-up diagnostic testing?
Do you have the results of the NIPT, the 13-week scan or the 20-week scan? And is there evidence that your child has a chromosomal or physical abnormality? If so, follow-up diagnostic testing is needed to understand the abnormality fully. The sonographer, midwife or doctor will tell you what options are available for follow-up diagnostic testing. It is up to you to decide whether you want to have follow-up tests.
Which follow-up tests are offered depends on which test you had first and how far along you are in your pregnancy:
| Comprehensive ultrasound scan | Blood test | Chorionic villus sampling (from week 11) |
Amniocentesis (from week 15) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NIPT | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| 13-week scan | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| 20-week scan | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
In a chorionic villus sampling test, the doctor will take a small piece of the placenta for testing. This can be done after week 11 of pregnancy.
In an amniocentesis, the doctor will remove a small amount of amniotic fluid for testing. This can be done after week 15 of pregnancy.
The disadvantage of these options is that there is a minor risk of miscarriage after chorionic villus testing or amniocentesis. This occurs in 2 out of 1,000 women.
The cost of follow-up diagnostic testing will sometimes be deducted from your insurance excess.
You can be referred to a prenatal diagnostic testing centre for an appointment. You will not have to decide until after that. You may also decide that you do not want follow-up testing.
Data and privacy
What happens to my data?
If you choose to take part in prenatal screening, your care providers will keep your details about this in your medical records. This is required by law.
Your data and the results of the NIPT and the ultrasound scans will also be stored in a national information system (Peridos). This is necessary for the screening tests to go smoothly. Data and results are also used to check whether care providers and laboratories are doing their jobs properly.They are also used to estimate how many people opt for prenatal screening during their pregnancy.
The national information system is secure. If you still prefer not to have your data stored in that system, tell your midwife. The midwife will ensure that your data stored in the national information system will be deleted after you give birth; only data that cannot be directly linked to you will remain in the system. Once that happens, you will be anonymously included in the statistics, but no one will be able to trace which data are yours.
After your blood has been analysed in the NIPT laboratory, some blood may be left over. The NIPT laboratory stores the blood samples and associated data in a well-secured system.
Then you will automatically take part in the scientific IMITAS study. This means the researchers are permitted to use your data in the future (up to 15 years). You will be given a consent form to sign before taking part in the study. Would you like more information about this? Go to www.13wekenecho.org (website in Dutch).
During the counselling session, your midwife or the scientific researchers will ask if you consent to your data being used in future scientific research. The same will apply to any blood left from your blood sample, if you chose to have the NIPT. The data also includes details of any follow-up diagnostic testing and your child’s health after birth.
Blood samples are stored for a period of 1 year. If you give consent for any leftover blood to be stored and used for scientific research, then that blood will be stored for a period of 8 years.
If you do consent to scientific research, the researchers cannot see your name and address. They do not know who the data and blood belong to.
If you want to withdraw your consent to future scientific research, tell your midwife. The midwife will notify the appropriate authorities.