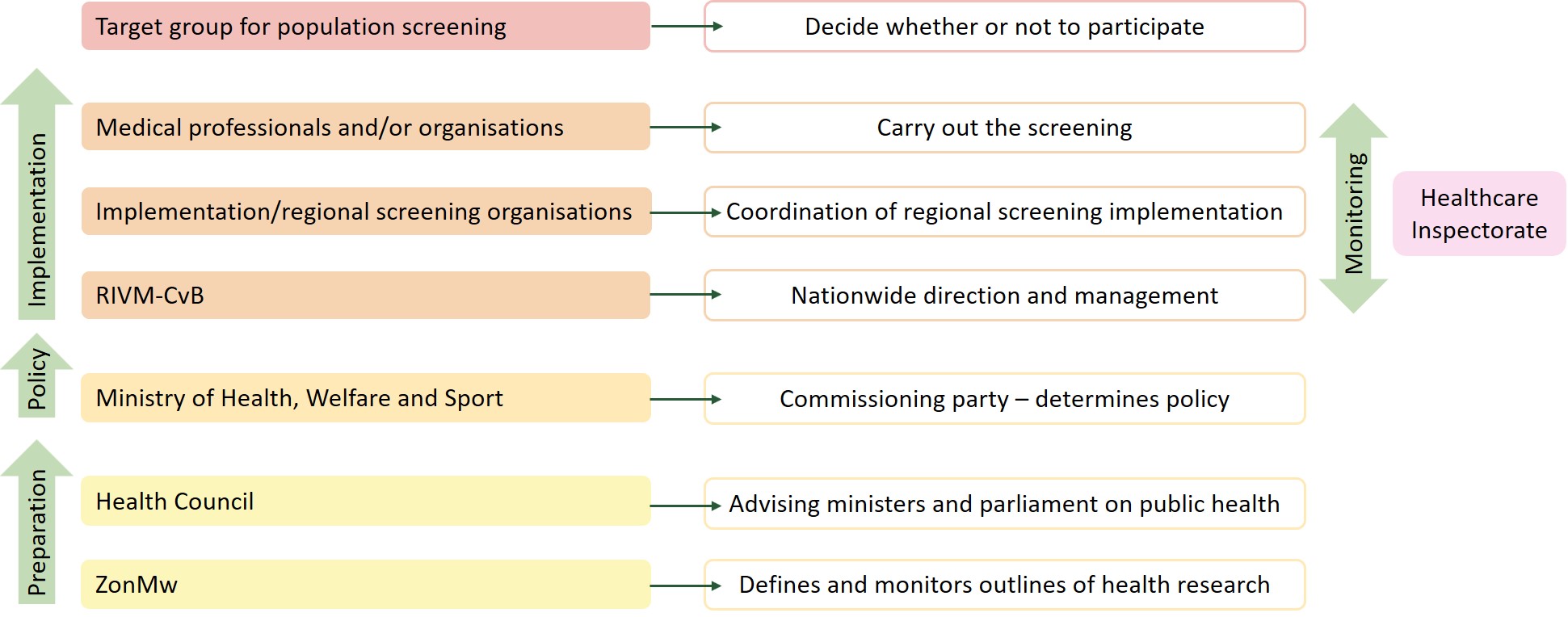
The Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport commissioned RIVM (Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu) with the nationwide direction and supervision of prevention and screening (onderzoek) programmes. RIVM set up the Centre for Population Screening (CvB) in 2006 to carry out that task.
RIVM's role
RIVM (Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu) has a nationwide coordinating role, meaning it ensures that high-quality population screening (onderzoek) is provided for the participants and that it is easily accessible and affordable, therefore creating the optimum circumstances for those participating in population screening. RIVM connects parties in policy making and implementation. It organizes and supports the network proactively and aims to further develop current population screening and successfully implement new screening. More information
Key players among the authorities
Various governmental bodies are involved in the preparation, modification and reassessment of population screening (onderzoek). The Health Council of the Netherlands and the Netherlands Organisation for Health Research and Development (ZonMw) have a task that is primarily preparatory, for new population screening programmes and far-reaching changes to the existing programmes. The Health Council is an independent scientific advisory body and ZonMw (Nederlandse organisatie voor gezondheidsonderzoek en zorginnovatie) is an independent executive body that finances research into health.
RIVM (Rijksinstituut voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu) provides advice on the setup and aspects of the implementation. Final decision-making is done by the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport (VWS). The Healthcare Inspectorate has a supervisory role. More information about the tasks of each governmental body can be found in the policy frameworks at the bottom of this page.
The Population Screening Act
The Netherlands is one of the few countries worldwide where the preconditions for screening (onderzoek) are legally established in the Population Screening Act (WBO). This Act was introduced in 1992 and provides protection against unnecessary or harmful screening programmes. It outlines all the requirements that have to be met to ensure the quality of the screening.
A WBO (Wet op het bevolkingsonderzoek) permit is required in order to execute a screening programme. The WBO therefore monitors all screenings and not only those of the National Population Screening Programme. If the permit is issued, it means that the screening is scientifically sound, that it is in accordance with legal rules for medical treatment and that the expected efficacy of the population screening outweighs the risks to health.
Implementation of a new screening programme
What steps are taken before a screening programme can be introduced nationwide? The screening programme for bowel cancer is the most recent addition to the National Population Screening Programme. The phased roll out started in 2014 but the entire realisation process took 13 years. An overview of the implementation process and the involved parties can be found in the factsheet:Lessons learned from the introduction of the colorectal cancer screening programme in the Netherlands.